Tradition‘s Zugzwang
The Impact of Digitalization and AI on Organizations and People
In an era defined by rapid technological advancements, organizations face the challenge of adapting to the profound changes brought about by digitalization and artificial intelligence (AI). Often, however, companies fall into the trap of tackling new, complex problems using outdated strategies. This traditional approach, which may have been effective in the past, increasingly proves to be an obstacle in an environment that demands flexibility, agility, and innovative thinking.

Sebastian Schurig

Marie Oldenburg
Digitalization and AI do not merely offer new technical capabilities. They also transform how people collaborate and how organizations are structured. To avoid falling behind, organizations must adapt their structures, processes, and culture to these new realities. This paradigm shift means that old methods are often no longer sufficient to address the complexity and dynamism of today's world. It requires a fundamental realignment that goes beyond the mere implementation of new technologies and encompasses the entire system - from organizational structure to human collaboration.
However, this approach is rarely implemented. Often, only the new technologies are utilized or implemented. This is one reason why around 70% of all change projects fail to meet their objectives (Jessl & Heinze 2023). Quick fixes are frequently presented, which can only produce superficial effects. If companies truly want to sustainably implement digitalization and AI, it is a strategic issue that impacts the entire organization. To achieve this, the organization's resistance to change must be overcome.
"Problems cannot be solved with the same mindset that created them." (Albert Einstein)
Organizational Resistance to Change: Obstacle or Necessity in the Age of AI and Digitalization?
Resistance to change is a common practice in many organizations, designed to maintain the stability and continuity of business operations. It protects established processes and structures from abrupt or uncoordinated changes that could endanger efficiency or quality. In an environment that demands continuous innovation through AI and digitalization, however, this resistance to change can be a double-edged sword.
Change resistance safeguards proven processes and ensures the reliability of operations, which is crucial for daay-to-day business and maintaining quality standards. By carefully evaluating changes, potential risks arising from uncontrolled adjustments can be mitigated. This is especially important in areas where errors could have serious consequences. Change resistance helps preserve valuable cultural elements within the organization that have developed over time and significantly contribute to the company’s identity and success.
This is particularly important in areas where errors can have severe consequences. Change protection helps preserve valuable cultural elements within the organization that have developed over the years and significantly contribute to the company's identity and success.
Yet, an excessive focus on resistance to change can hinder innovation processes, as new technologies like AI often require quick adaptations and experiments to be successfully implemented. In a dynamic environment shaped by digitalization, change resistance can slow down the necessary speed in decision-making and adaptation, thus impairing competitiveness. Organizations that lean too heavily on resistance to change risk losing the ability to respond quickly to new market demands or technological shifts, which often puts them at a disadvantage compared to more agile competitors.
While resistance to change has played an essential role in ensuring stability and continuity throughout organizational history, a balance must be struck in today's digital age. Protective mechanisms should be designed in a way that does not sacrifice adaptability for the sake of stability. Companies must be able to react flexibly to changes without compromising their core structures and values. Finding the right balance between necessary protection and openness to innovation is crucial for success in the rapidly evolving landscape of digitalization and AI.
Breaking Traditions: How to Disrupt Tradition to Enable Successful Change
As mentioned earlier, around 70% of change projects fail to achieve their goals (Jessl & Heinze 2023). Based on the eight reasons for change project failures identified by Kotter in his classic "Leading Change" (1996), BearingPoint's 2021 survey of 300 change managers identified six key areas where errors can lead to project failure:
- Culture/Mindset: Emotional resistance due to a lack of understanding
- Leadership: Lack of leadership and support
- Communication: Lack of clarity
- People/Skills: Limited resources and insufficient know-how
- Structure/Processes: Lack of alignment with change
- Implementation: Lack of vision, strategy, goals, and a well-defined roadmap
One factor that can lead to failures in all these areas is the tendency to address new challenges brought by changes using old approaches. Particularly with disruptive changes, which are becoming more frequent in our fast-paced world, it is essential to question traditional ways of thinking and problem-solving methods. This does not mean that everything old was wrong or that the approach to change was ineffective in the past.
It simply means that the prevalent methods and tools are no longer suitable for the nature of today's changes. This fine line between breaking traditional patterns and embracing new approaches to successfully implement disruptive changes like digitalization or the increased use of AI, while simultaneously valuing past achievements, requires a systematic and thoughtful change strategy.
The following four key strategies can help achieve this:
1. Promote Cultural Change and Create Innovation-Friendly Structures
Changes in the digital environment, whether through virtual collaboration or the use of AI, impact not only employees and their daily work but also the sense of teamwork, the work culture, and the requirements for leadership. Corporate culture plays a central role in the successful implementation of change. It is important to foster a culture that supports openness to new ideas, an innovative spirit, and a willingness to take risks. Leaders and change agents are especially crucial in this process; they must lead by positive example, demonstrate the desired openness, encourage and reward innovation, and view mistakes as learning opportunities while creating a positive error culture and an experimental atmosphere. Key qualities include empathy, patience, and the ability to approach changes and innovations with a positive mindset and manage them proactively.
Beyond leadership, general organizational structures also play a critical role in managing change. Innovation labs and pilot projects can be valuable in testing new ideas and technologies in a small, controlled environment. Collaboration within interdisciplinary teams can bring together different perspectives and skills, leading to the development of creative solutions. The use of agile methods and frameworks can further enhance flexibility and adaptability in response to change.
2. Turning Employees from Affected Parties into Active Participants
One of the main reasons for the failure of change projects is resistance and concerns from employees. This is especially true when they feel that their past work is being questioned or criticized, or even fear that their jobs may be at risk due to the use of digital technologies or AI. In such cases, transparent communication management is essential. Actively involving those affected in the change process helps to alleviate fears, address questions early on, and increase acceptance.
Additionally, it is crucial to empower employees to prepare themselves professionally for the changes and to engage in continuous learning. The pace of digitalization is advancing at a tremendous speed. Ongoing development programs, training, and education in both technical and soft skills are essential to maintain motivation and prevent change fatigue.
3. Ensuring a Modern Technological Infrastructure
Remote work and virtual collaboration have become indispensable parts of today's work environment, especially since the COVID-19 pandemic. Teams now work across geographical boundaries using digital tools like Slack, Microsoft Teams, or AI-supported project management software. It is essential to provide the necessary training and support to employees in this area.
In addition to supporting employees, it is equally necessary to adapt the technological infrastructure to meet changing needs – this includes, among other things, modern tools and technologies such as cloud solutions and collaboration tools, the implementation of data analysis tools to quickly make informed decisions, as well as integration into existing systems and processes, and the provision of powerful work devices.
4. Providing Continuous Learning Opportunities and Enabling Adaptability
In our dynamic world, change is a continuous process. To be prepared not just once but to implement and sustain the strategies mentioned, it is essential to regularly review the status quo and current methods and work practices—through feedback loops, for example - compare them with other companies, identify best practices, and create a forward-looking, strategic plan to stay ready for future developments.
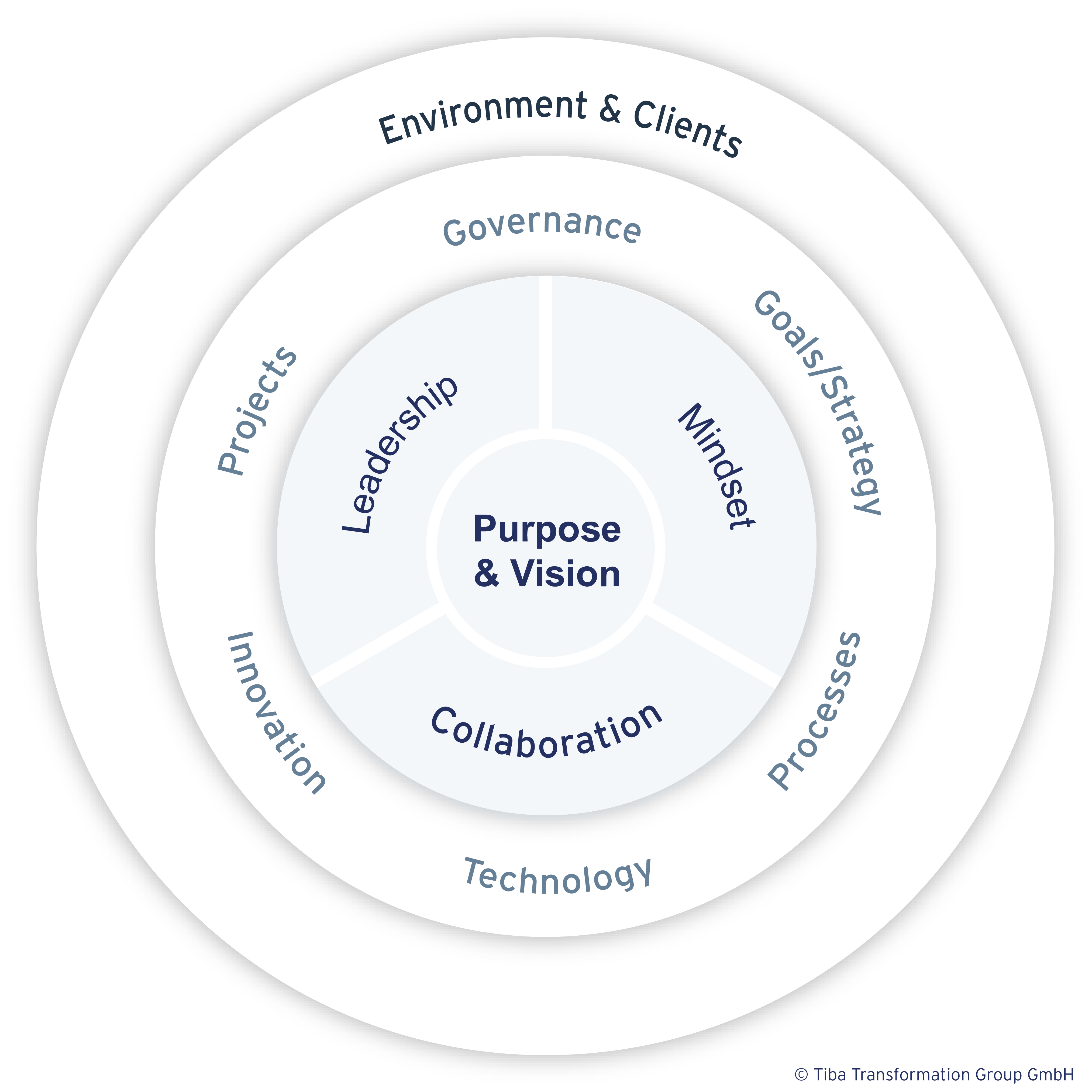
Figure 1: The Tiba Transformation Wheel® (own representation)
Practical Examples
Successful Digitalization through Active Employee Engagement
As part of automation and digitalization, the entire working approach of a department in a corporation must be completely transformed. This transformation impacts all elements of the Tiba Transformation Wheel® (see Figure 1).
The difficulty in any transformation is always finding the right starting point. Attempting to initiate change in all areas at once leads to instability, is unhealthy, and poses a risk to the company. The company's existing patterns were characterized by a focus on functions, clear responsibilities, limited decision-making power for knowledge holders, and a low motivation rate - the negative side of the lived tradition in this organization.
Digitalization and automation required the full potential of the company and its employees. The first attempt to implement these changes using the traditional toolkit failed. Dissatisfaction grew, successes were absent, and the entire digitalization effort was questioned - at least by the employees. A different approach was needed to break these patterns. Therefore, a restart of the initiative was launched, adopting a different strategy that enabled and required an iterative approach, prototyping, and a digital mindset.
Initially, a heat map of the key topics was created, including prioritization. The process of creating this heat map was designed to reflect how the company intends to work in the future. Instead of being dictated from the top, it was developed in collaboration with the employees. For the implementation, cross-functional teams were formed to work on and execute the topics. These topic clusters covered all areas of the Tiba Transformation Wheel®. The focus was not only on the topics themselves but also on leadership understanding, a collaborative mindset, and behavior. Structural changes were also jointly decided upon and implemented, resulting in new processes, new organizational structures, and new roles and responsibilities.
Decisions are now made faster, and mistakes are seen as learning opportunities. These are just a few of the outcomes. It becomes evident that digitalization enables the transformation of an organization and its realignment. Its effects go beyond digitalization itself.
Sustainable Cultural Change through Lean Organization and Competency Development
After the departure of the founder of a large industrial company and the appointment of two new board members, a new corporate culture was needed. The previous approach of unilateral decision-making by the owner and founder could not be continued under the new managers. To facilitate this transformation, the company aimed to establish an effective lean organization. This approach involved not only defining and aligning efficient (production) processes but also transforming the entire corporate culture. Previously, it was possible to directly discuss ideas and topics with the owner and quickly receive decisions on matters and potentially risky investments. However, a manager-led organization requires different decision-making processes. To make this as streamlined as possible, the concept of a "lean organization" was implemented.
One of the key levers in this transformation was the development of leadership skills, which involved a significant focus on competency building. Foundational steps were established at all levels to support the transformation into an efficient organization. The list of necessary new skills was developed by the employees themselves and was prioritized together with the board. This initiative included not only methodological skills like change management and coaching but also the experience of new models of collaboration and the personal development of the leaders. The board not only supported this effort but also led by example, acting as role models for the change. This foundation enabled the company to move forward with the substantive improvement of production processes and collaboratively explore and implement automation initiatives.
Conclusion
In a world increasingly shaped by digitalization and artificial intelligence, organizations must confront the need to question and adapt their traditional approaches. Classical methods for problem-solving or managing change are no longer sufficient to meet these new challenges. While stability and continuity are valuable for ensuring security, they can also be obstacles when it comes to innovation and necessary adaptations. Organizations must therefore strike a balance between preserving proven structures and remaining open to new possibilities.
The need for a systematic and well-thought-out change and transformation approach is highlighted by the high failure rate of unstructured change projects. It's essential to focus not only on technological adaptations but also on fostering cultural and structural changes. Actively involving employees and stakeholders through an iterative approach, ensuring a modern technological infrastructure, and providing continuous learning opportunities are just a few examples of critical success factors in change and transformation projects.
Digitalization and artificial intelligence offer the opportunity to comprehensively renew organizations, positioning them to be modern and future-proof, provided they are approached strategically and holistically. Only in this way can companies secure their competitiveness in a dynamic environment over the long term.
Literature
BearingPoint (2021). Change Management Studie: Verankerung von Wandel in Organisationen. https://www.bearingpoint.com/de-ch/insights-events/insights/change-management-studie-2021/ [retrieved on July 4th, 2024].
Jessl, R. & Heinze, I. (2023). Misserfolge im Change. https://changement-magazin.de/interview/misserfolge-im-change/ [retrieved on July 4th, 2024].
Kotter, J. P. (1996). Leading Change. Harvard Business Review Press.